The fastest way to get the answers you’re looking for is to give our team a phone call. However, we understand that some people may be busier than others, or you simply prefer to research online first. In either case, we want to make your experience as stress-free as possible. That’s why we’ve compiled some of our most commonly asked questions and their answers below!
How Do I Find the Best Place to Get Dental Work Done?
You’ll first need to determine what you find most important for you, which can be a mixture of things like hours, credentials, location, cleanliness, insurance/payment, fees, and safety. The type of dental treatment you’re looking for is also crucial, such as if you require dentures, dental implants, teeth whitening, Invisalign, or simply a routine dental checkup and cleaning. Some practices may be better suited for specific services. Finally, be sure to get a feel for the practice and the team so that you know how they interact with their patients. For instance, our staff focuses heavily on understanding each patient’s dental goals and concerns so that we can tailor their care to their unique needs. You can also read about the doctor and our team members from their bios on our website.
How Can I Make a Same-Day Appointment With a Dentist?
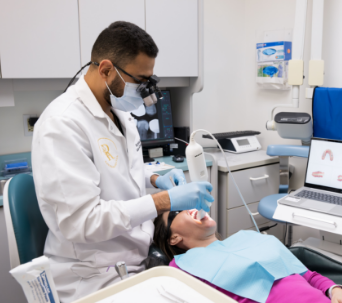
The quickest way to schedule a same-day appointment with a dentist is by calling the practice directly. If you send the team an email, our office might not be able to provide an answer as quickly as possible. Furthermore, calling us by phone is more efficient because it lets our team members better understand your specific situation so that they can get you scheduled for the best care sooner rather than later. Also, most dental practices have an extra exam room so that they can address dental emergencies as well as same-day appointments. During your visit, our team will evaluate your situation, eliminate the source of pain/discomfort, and then create a plan for future treatment. In some cases, you might be able to undergo advanced care during a same-day visit.
What Level of Education Is Required to Be a Dentist?
Dentists throughout the United States usually require either a Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD) or a Doctor of Dental Sciences (DDS) from one of the accredited dental schools in the country. In order to get into these schools, one typically needs to earn a bachelor's degree, usually in a major focused on math and science, and with very high grades. Then, they’ll need to undergo 3 years of a combination of classroom and hands-on learning. Afterward, some dentists continue their education by obtaining 1 of 12 specializations recognized by the American Dental Association, which can take an additional 3 or more years of training to acquire. To retain their license, dentists need to complete a certain number of hours in continuing education courses every year.
How Many Dentists Are in Raynham, MA?
With a quick Google search, you can find that there are around 180 dentists in and around Raynham, MA. However, generally speaking, a good rule of thumb is that there should be 1 dentist for every 2,000 people in a population. For instance, a city with 66,000 people will typically have 30 to 35 dentists. However, if you want to have a more concrete answer, you can call or visit our team with your question. If you’re also interested in cosmetic dentistry, dental implants, or dentures, you can always speak with Dr. Al, who has decades of experience providing comprehensive, comfortable, and personalized dental care!